More and more WordPress site operators are deciding to do so in 2025, Deactivate AMP. Modern hosting technologies and new performance standards make the Google framework largely superfluous and even a hindrance to design freedom, tracking and monetization.
Key points
- Design restrictions and limited functions reduce the user experience on AMP pages.
- Powerful managed hosting delivers comparable loading times - without AMP.
- Google no longer favors AMP pages in the ranking.
- Trackingadvertising and individual elements can be better implemented on classic sites.
- The Changeover enables complete brand presence and flexible further development.
It also shows that many developers and marketers want new degrees of freedom that AMP simply cannot offer. For example, anyone who wants to use an elaborate, interactive web design, complex conversion tools or highly personalized elements such as targeted remarketing will quickly reach their technical limits with AMP. Especially at a time when content creation and layout design are becoming ever more closely intertwined, detailed design options are more important than ever.
In addition, marketing and SEO strategies have changed significantly in the meantime. Old shortcuts, as AMP was for a long time, no longer work, and organic growth depends more than ever on good content, clever technical control and an optimal user experience. So if you rely on AMP, you risk not being able to keep up creatively - a major shortcoming in the competition for user attention.
What is AMP and why was it introduced?
AMP, which stands for "Accelerated Mobile Pages", is a framework supported by Google. The aim was to make mobile websites very fast through greatly reduced HTML, CSS and JavaScript functionality. For many, this meant better automatic loading times and therefore better visibility in mobile searches.
Those who activated AMP in the past hoped for more traffic and visibility. However, this also came with many restrictions. Functional freedom was lost - in favor of speed. Today, however, other tools are available that enable both: Speed and function.
A key aspect of the introduction of AMP was that Google made mobile speed one of the core requirements for a good ranking. In the early years, AMP was a kind of turbo solution for publishers to ensure lightning-fast content delivery and benefit from new mobile services such as the "Top Stories" carousel. Over time, however, it became clear that AMP itself had significant design limitations and sometimes displayed confusing URLs to users in the browser because the content was served via Google's own AMP cache. Today, modern hosting solutions, caching plugins and optimized themes often offer a user experience that is just as fast, yet considerably more flexible.
In 2025, it is also generally recognized that "mobile-first" is no longer just a buzzword, but the standard for web projects. In this context, AMP seems like an anachronism: although it solves the speed problem, it restricts creative freedom. With newer technologies such as Progressive Web Apps (PWA), websites can also load extremely quickly and also offer offline capabilities or push notifications - without being subject to AMP-typical restrictions.
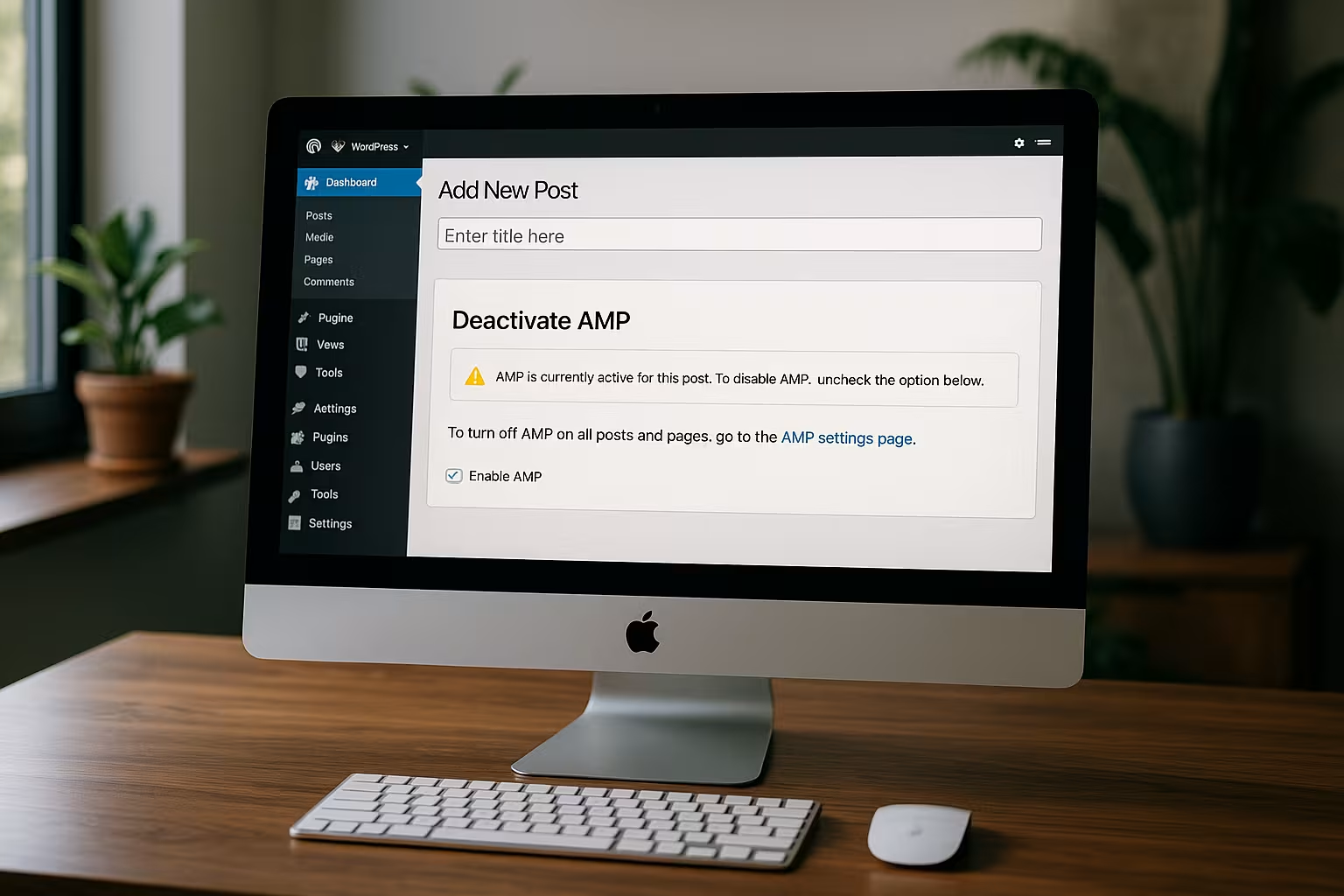
Why deactivate AMP 2025?
The reasons for deactivating AMP in 2025 are of a technical and strategic nature. The HTML-limited pages are no longer competitive. Modern approaches in WordPress, such as mobile lazy loading, core web vitals and image optimization, have functionally overtaken AMP.
I can hardly use JavaScript under AMP. This makes it impossible to integrate chat functions, pop-ups or personalized content, for example. Even advertising and analysis tools such as Google Ads or Matomo can only be used to a limited extent.
In addition, AMP repeatedly causes a loss of trust among users because the visible URL runs via the AMP viewer. Google itself has also abolished the AMP label and the preference in the top stories carousel, which further reduces its relevance.
Another aspect is that AMP has not been developed over the years as many had expected. While WordPress cultivates its own ecosystem of plugins, themes and performance tools, AMP is limited to its own, sometimes complex set of rules. However, most website operators want maximum flexibility in order to integrate advertising space, forms, interactive features or remarketing pixels with precision. If you deactivate AMP today, you will not only save yourself maintenance work for several page versions in the long term, but will also have a much clearer database for conversion optimization.
Performance: Hosting beats AMP
AMP was introduced to display websites extremely quickly on mobile devices. But this argument is becoming less and less valid in 2025. Because hosting offers such as that from webhoster.de show that loading times under 2 seconds are possible today without AMP.
The decisive factor is a system mix of caching, image optimization, script minimization and CDN. Together with a high-performance hosting service, this creates a site that is faster and more flexible than any AMP solution.
Managed hosting solutions in particular can tailor infrastructures specifically to WordPress. This means that certain PHP settings, database configurations and caching mechanisms are perfectly coordinated. The increasing availability of edge servers around the globe also ensures that users access the site from a server that is geographically close to them - which further optimizes overall performance. Within WordPress, lazy loading for images or asynchronous loading of scripts can be activated to present content even faster.
In practice, this means that if you take your time and choose your hosting carefully, you can easily achieve top scores in Google PageSpeed Insights or the Core Web Vitals without having to take the detour via AMP. Although this requires some investment and a certain level of technical understanding, the end result is a solution that is more individual, more flexible and more future-proof in the long term.

Ranking and SEO impact when switching off AMP
As soon as AMP is deactivated, the /amp versions disappear from the Google index. Traffic via these pages will therefore temporarily collapse. Nevertheless, the visibility in the search results remains - provided the page is fast and mobile-optimized.
Google attaches particular importance to the Core Web Vitals values in 2025. These can be monitored and improved without AMP - for example with the help of SEO plugins such as Rank Math or Yoast and tools such as PageSpeed Insights.
Studies show that not using AMP usually does not result in a lasting drop in visitors - if performance and user experience are right.
A precise analysis is particularly worthwhile for editorial pages that previously benefited greatly from the AMP display in Google News. If you have an already well-optimized mobile site, you rarely lose significant reach. On the contrary: articles are often ranked stably after a short transition phase because they offer a better user experience - without ugly redirect fragments or shortened elements. Users appreciate the improved overview in the design and seamless navigation.
SEO techniques have also evolved: With structured data, clean HTML5 and high-performance themes, you are well positioned for ranking algorithms. AMP is no longer a must. Google itself has accelerated this development by significantly reducing the special treatment of AMP pages and emphasizing the focus on loading speed and content relevance in other areas.
How to deactivate AMP in WordPress
Only a few steps are required to disable AMP in WordPress:
- In the admin menu click on Plugins click
- Search for and deactivate the AMP plugin
- Optional: Delete plugin and remove database entries
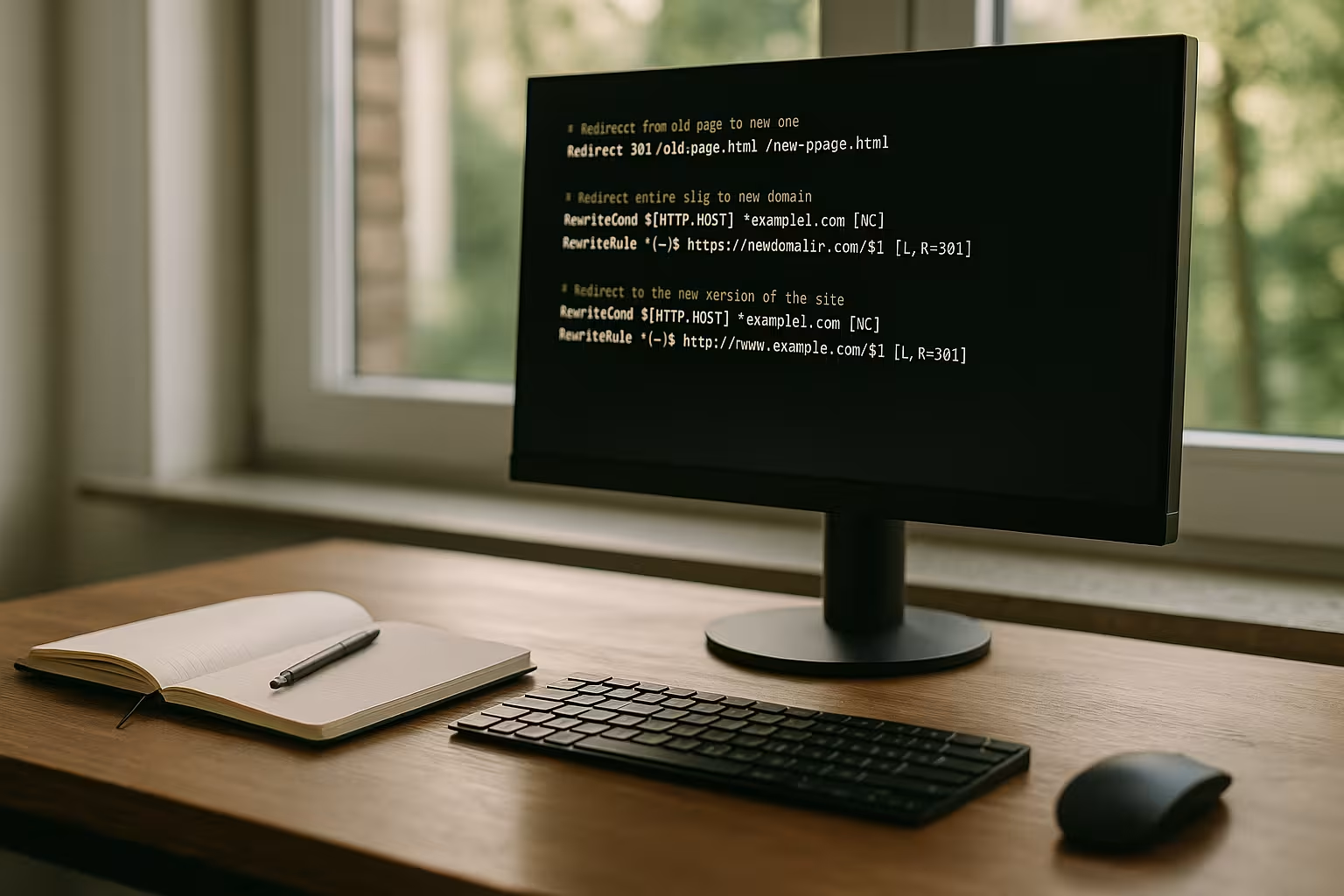
- Set up 301 redirects from old /amp URLs to regular pages
- Test mobile site functions: contact forms, advertising banners, tracking
- Check speed via GTmetrix or Lighthouse
I recommend using a staging environment for this. This allows you to test the effects of the changeover without risk.
At the same time, you should have checked the site structure. Many users redirect AMP pages via 301 to prevent a sharp increase in 404 errors. A clean redirect plan ensures the preservation of link juice and protects against ranking losses. Also, don't forget to monitor old AMP errors in Google Search Console and report them if Google continues to try to access these subpages.

Optimization tips for an AMP-free website
To do without AMP without sacrificing loading time or visibility, you should use modern performance techniques. Here is a comparative table with typical measures:
| Optimization measure | AMP required? | Alternative technology |
|---|---|---|
| Fast loading time | No | Managed hosting, caching, CDN |
| Mobile-friendly layout | No | Responsive themes with Gutenberg or Elementor |
| SEO for mobile devices | No | Core Web Vitals + Mobile Optimization |
| Tracking & Advertising | Yes, limited | Fully controllable without AMP |
| Design freedom | No | Full CSS and JS control on Classic pages |
The table clearly shows how versatile modern WordPress websites can be without AMP. Whether you want a smooth mobile layout, complex menu structures, sophisticated performance optimization or diverse analysis tools - all of this is possible without AMP, provided your hosting and plugin environment is designed accordingly. It is advisable to regularly scan your own site, for example with Lighthouse or GTmetrix, to identify optimization potential. Paying attention to image formats such as WebP can also significantly reduce the page size.
For whom is the switch worthwhile?
Doing without AMP brings many noticeable advantages. I particularly recommend it for:
- Operators of online stores that use checkout processes, discount campaigns or filters according to measurement rules
- Content websites that work heavily with elements such as surveys, videos or ads
- Agencies that need pixel-perfect branding and complete control over technical options
Bloggers also benefit from the switch. For example, anyone running an affiliate business in the background or integrating pixel-perfect advertising banners for cooperation partners can better control how large the banner area is, where it appears and which scripts are executed behind it without AMP. It also opens up the possibility of integrating interactive tools to involve the reader in surveys or quizzes, for example, which can increase dwell time and engagement.
In addition to pure functionality, branding is also playing an increasingly important role. AMP pages often appear very simplified and are restricted to Google's layout and CSS specifications. However, brands want to position themselves clearly and differentiate themselves. With a creative, mobile-optimized WordPress site, you can stand out from the competition both visually and in terms of content. In the long term, this strengthens brand loyalty and trust among visitors.

Important steps after deactivation
After the shutdown, the website should be technically checked and optimized in parallel. Tools such as GTmetrix, WebPageTest or the Chrome Audits tab can help with this. It is then recommended to use Google Search Console to remove outdated AMP URLs.
The integration of an SEO plugin that correctly prepares structured data is also an advantage. Loading times of less than 2 seconds and a time to first byte (TTFB) of less than 200 ms should also be the goal. Good hosters make this plannable.
For all those who already use a performance plugin such as WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache or WP Fastest Cache, it makes sense to check the settings again. Minimizing and combining CSS and JavaScript files in particular can have an immense impact on the actual loading speed. A carefully selected caching plugin can partially automate the tasks and ensure constant performance. At the same time, care must be taken to ensure that images and other media components are displayed efficiently. Hosting providers are now increasingly supporting the Brotli compression method, which provides even better performance than the well-known Gzip.
If you have visitors in different parts of the world, you can also use a CDN. This is by no means AMP-dependent, but works with any WordPress site. When AMP is deactivated, a CDN is often the optimal building block for serving an international audience at a consistently high speed. Plugins such as Cloudflare Flexible SSL or the setting of HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 further increase efficiency and stability.
How to stay permanently AMP-free and successful
Those who have deactivated AMP need not fear a relapse. On the contrary - with a fast host, responsive theme, cache plugin (e.g. WP Rocket) and a content delivery network such as Cloudflare, you are ideally positioned.
It is crucial to keep everything up to date on a regular basis and to critically analyze the site structure, server and media formats. Popular WordPress plugins for SEO, performance and security help with this task.
A holistic view of the user experience is essential: site navigation, readability, loading times and accessibility all play together. AMP limited this in part by only allowing a minimal range of functions. Without AMP, on the other hand, you can add new features such as chatbots, interactive call-to-action elements or dynamic adjustments to user behavior at any time. A/B tests can also be implemented much more easily and in greater detail, as no second simplified page version has to run permanently.
Continuous analysis of your visitor flows is also important: check how user behavior develops on mobile, tablet and desktop devices. Sometimes a special design feature ensures better conversion rates on mobile smartphones, while it can be irritating on tablets. With AMP, such individual adjustments would hardly have been possible, as the framework sets such flexibility limits. Without AMP, however, you can adapt layouts to any device or test alternative versions without the barriers of the AMP framework.

Summary: AMP was yesterday - flexibility counts in 2025
Disabling AMP is more than an option in 2025 - it makes sense. AMP's performance advantage is history. Those who rely on modern hosting, a well thought-out page speed and technical freedom today will benefit across the board.
I myself have deactivated AMP on several pages and thus improved conversion rates, loading times and user retention. The future lies in flexible technologies and self-determined page structure - you no longer need a restrictive framework for this. Now is the right time to switch.



